Perfect Chemical Formulas With Coefficients

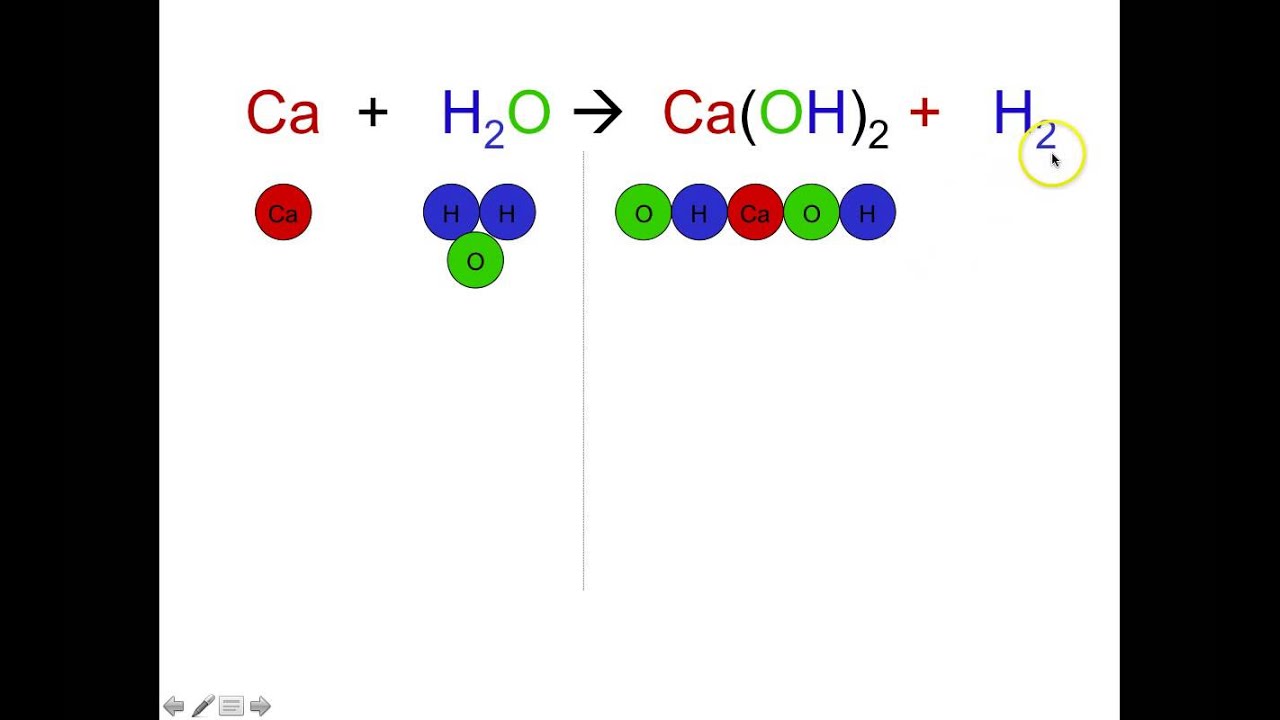
A coefficient is a number placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula.
Chemical formulas with coefficients. Here is the example equation again. 1 Consider the reaction that is represented by the following chemical. It shows how many atoms or molecules of the substance are involved in the reaction.
There are subscripts which are part of the chemical formulas of the reactants and products. Coefficients are the numbers in front of the formulas. In a chemical equation the reactants are written on the left and the products are written on the right.
In Chemistry the coefficient is the number in front of the formula. It is common practice to use the smallest possible whole-number coefficients in a chemical equation. The coefficients next to the symbols of entities indicate the number of moles of a substance produced or used in the chemical reaction.
Fe Au Co Br C O N F. A chemical formula is a way of expressing information about the proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound using a single line of chemical element symbols numbers and sometimes also other symbols such as parentheses dashes and brackets. What is the purpose of a coefficient.
A coefficient is written directly before the chemical formula with which it is associated. Ionic charges are not yet supported and will be ignored. In a chemical formula the letters represent the atomic symbol of each atom.
The subscript lower represents the number of each atom while the superscript higher represents the charge on a given atom. If no coefficient is shown a one 1 is assumed. A coefficient before a chemical formula represents that many units of the molecule.