Casual Kinetic Energy Rearranged For Mass
G P E Equation Rearranged.
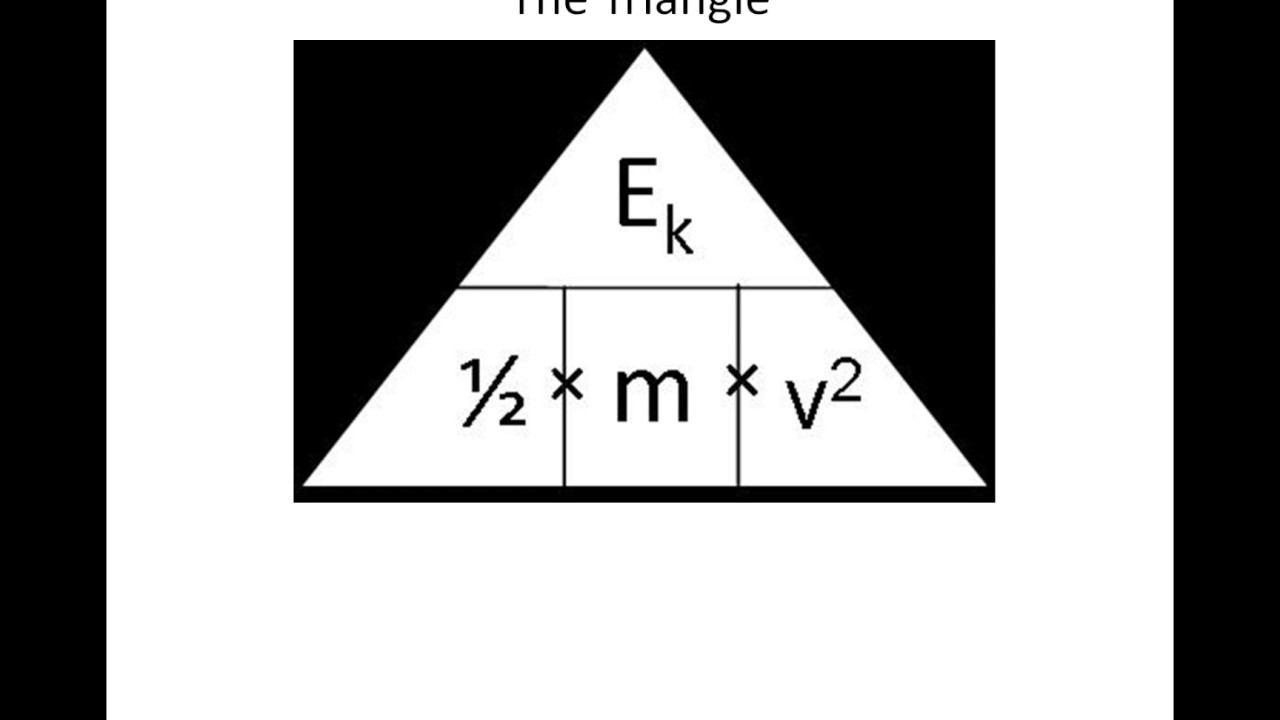
Kinetic energy rearranged for mass. KE 12 mass x velocity². Therefore we dont need the second term and an objects kinetic energy is just K ½mv2 Derivation using calculus but now we dont need to assume anything about the acceleration. Mass is a factor in an objects kinetic energy but the velocity of the object is the dominating variable.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. To calculate kinetic energy use the equation. Kinetic energy for an individual atom can be calculated by the following equation where m is the mass and u is the speed.
Its much more computationally. If the object moves quickly the relativistic mass is greater than the rest mass by an amount equal to the mass associated with the kinetic energy of the object. Calculating kinetic energy The amount of kinetic energy in a moving object can be calculated using the equation.
M GPE g. Physics For Scientists and Engineers. K kinetic energy.
How do you rearrange the kinetic energy of mass. In classical mechanics kinetic energy KE is equal to half of an objects mass 12m multiplied by the velocity squared. Massless particles also have relativistic mass derived from their kinetic energy equal to their relativistic energy divided by c2 or mrel Ec2.
K kinetic energy. S ut ½ at2. G Kinetic Energy ½ mass x velocity2 KE 5 mv2 Units.