Casual Velocity Physics Formula

Here P is initial position and S is final position.
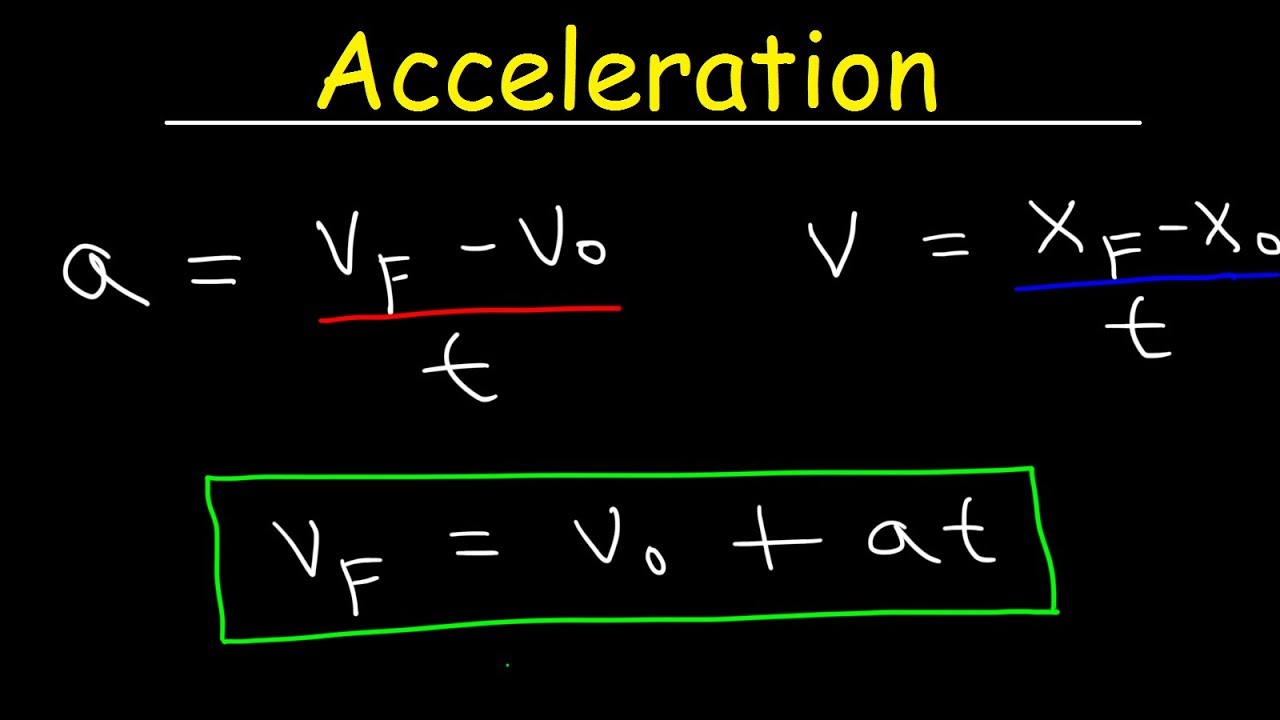
Velocity physics formula. The circular velocity of an object is calculated by dividing the circumference of the circular path by the time period over which the object travels. When it comes to the velocity equation it is stated as the change in the position of an object divided by the time. SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference Circular Motion continued v 2πr T v velocity r radius T period This formula gives the veloc-ity v of an object moving once around a circle of radius r in time T the period.
Volume ow time ˇpr4 8 l l r Terminal velocity. The distances traced in each intervals is say x1 x2 and x3 and the time required for the same is t1 t2 and t3 respectively. You can convert kmh to ms by dividing by 36 this is an exactvalue and has an infinite number of sig digs.
In simple words velocity is the speed at which something moves in a particular direction. Average values get a bar over the symbol. A velocity definition of physics is referred to as a vector measurement of the rate and direction of motion.
F 1 T f frequency T period The frequency is the number of times per second that an object moves around a circle. Velocity definition states that it is the rate of change of the objects position as a function of time. Weigh the object on the mass balance.
Velocity Formula Physics Velocity measurement is a very important computation used in mechanical physics. V 10 120. Electrons in a material due to an electric field.
It is also measured in m 2 Vs. Equating work and kinetic energy allows you to determine velocity from force and distance. Now recall the formula which is velocity displacement time.