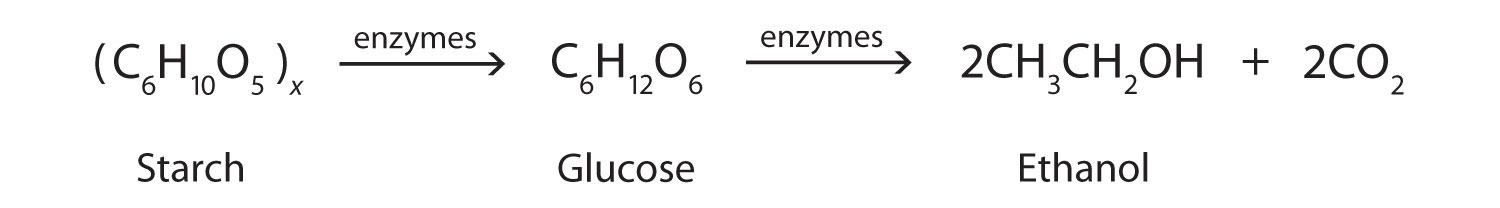Matchless Alcoholic Fermentation Equation

Facultative anaerobes are organisms that can undergo fermentation when deprived of oxygen.
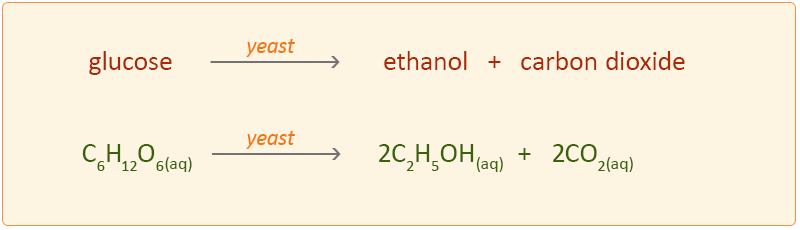
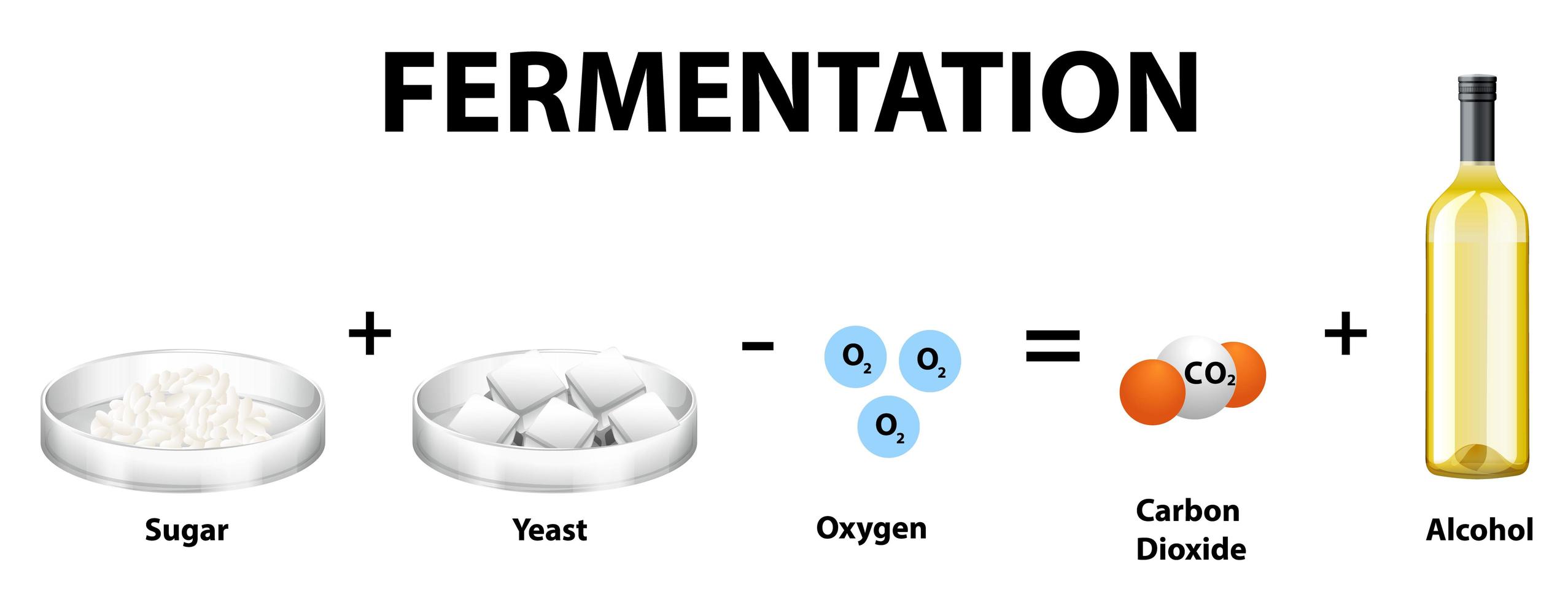
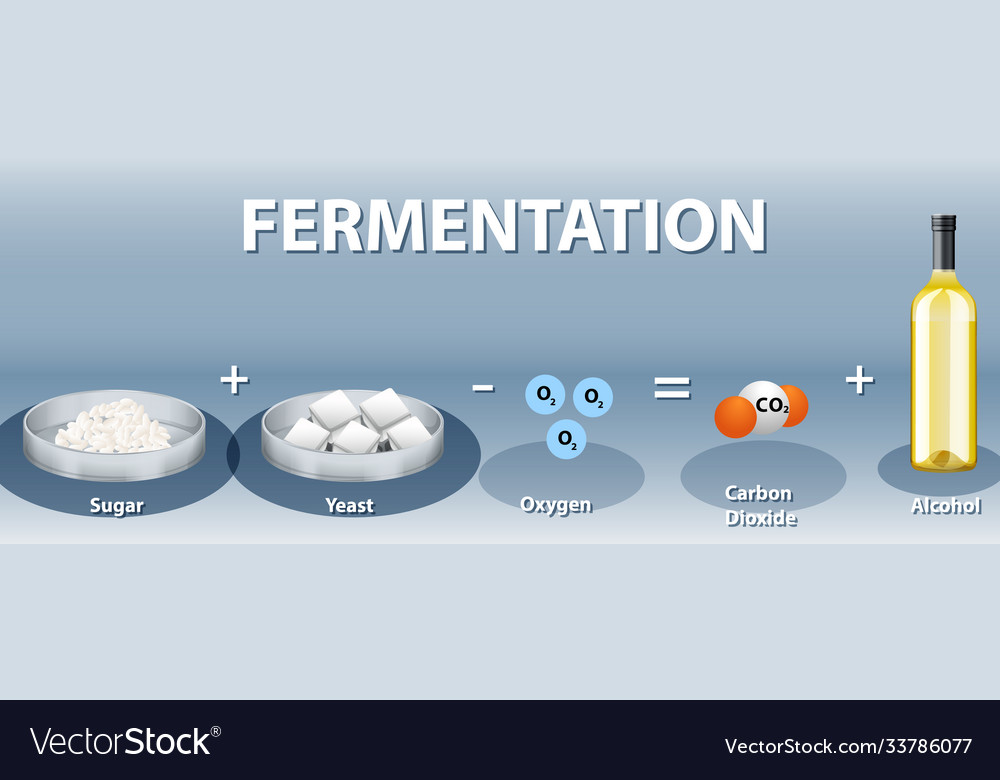
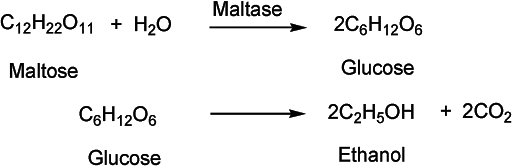
Alcoholic fermentation equation. Alcoholic fermentation is the oxidation of sugars to produce ethanol and CO2. Alcoholic fermentation is the main process that produces ATP in yeast cells. Alcoholic fermentation is the best known of the fermentation processes and is involved in several important transformation stabilization and conservation processes for sugar-rich substrates such as fruit and fruit and vegetable juices.
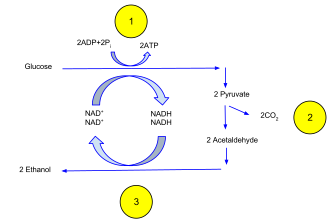
It is similar to lactic acid fermentation in that both processes occur in the absence of oxygen. Grapes to produce alcohol. Fermentation refers to the metabolic process by which organic molecules normally glucose are converted into acids gases or alcohol in the absence of oxygen or any electron transport chainFermentation pathways regenerate the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD which is used in glycolysis to release energy in the form of adenosine.
Jan 18 2021 alcoholic fermentation definition. Yeast is one example of a facultative. A type of fermentation wherein the end product is an alcohol eg.
What are three end products of alcoholic fermentation. The Lactic acid fermentation equation is usually described as. Alcoholic Fermentation is a type of fermentation in which carbohydrates mainly glucose are converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide molecules.
Hydrogen atoms from NADH H are then used to help convert acetaldehyde to ethanol. The yeasts for instance are used to ferment sugars in fruit juice eg. Carry out alcoholic fermentation.
The two types of fermentation are alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. It is caused by many yeasts and some mold fungi. The constants in Ballings formula are based on approximations of the amount of yeast produced during fermentation.