Casual Kinematics Meaning In Physics

Also called applied kinematics.
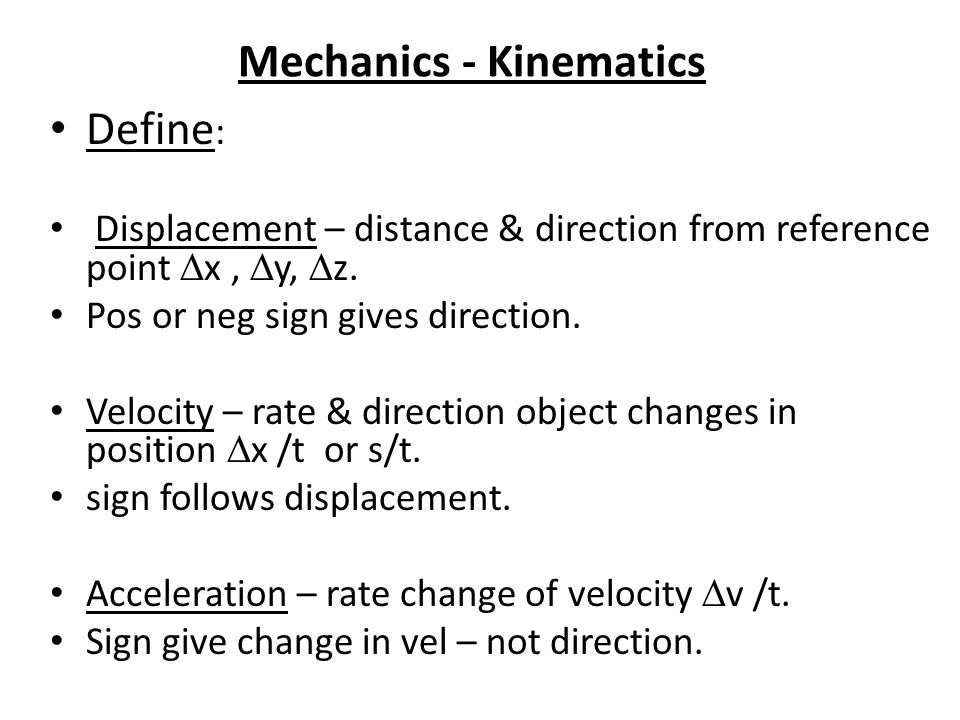
Kinematics meaning in physics. Kinematics branch of physics and a subdivision of classical mechanics concerned with the geometrically possible motion of a body or system of bodies without consideration of the forces involved ie causes and effects of the motions. Kinematics are often referred to as motion geometry. These equations link five kinematic variables.
We will start by introducing the concept of vector quantities. From there we will apply our knowledge to describing one-dimensional motion followed. Kinematics refers to the branch of classical mechanics which describes the motion of points objects and systems comprising of groups of objects.
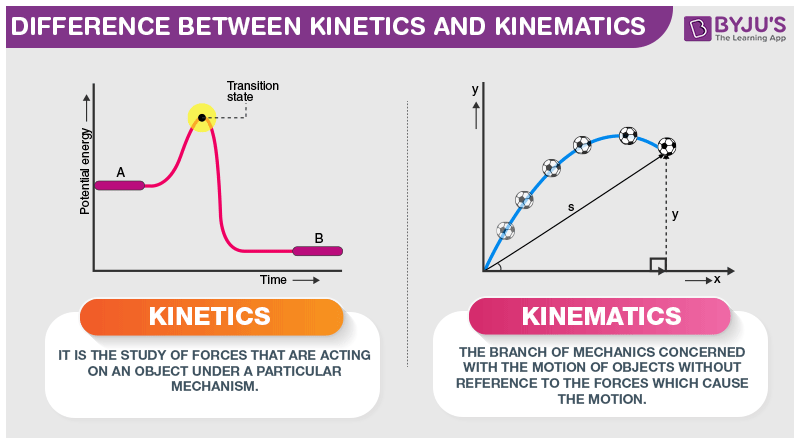
The theory of mechanical contrivance for converting one kind of motion into another. Calculus is an advanced math topic but it makes deriving two of the three equations of motion much simpler. In physics and engineering kinetics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the relationship between motion and its causes specifically forces and torques.
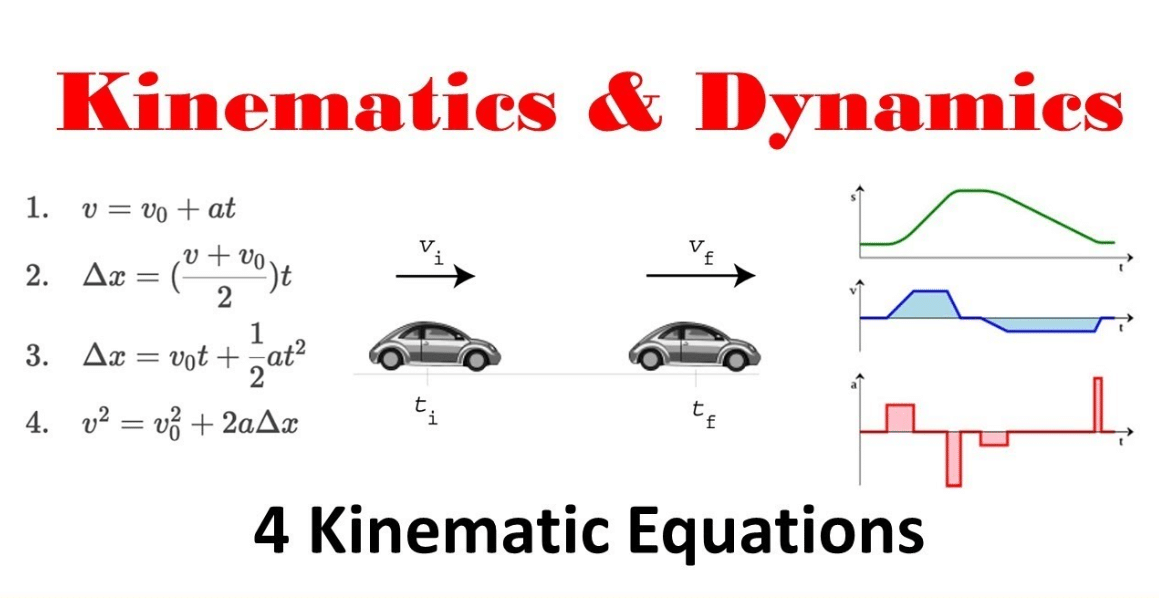
Kinematics one direction motion in physics is also called as 1-D motion or straight line motion 2-D motion or plane motion 3-D motion or space motion in this topic every basic concept for motion will be covered. Kinematics equations are a set of equations that can derive an unknown aspect of a bodys motion if the other aspects are provided. Take the operation in that definition and reverse it.
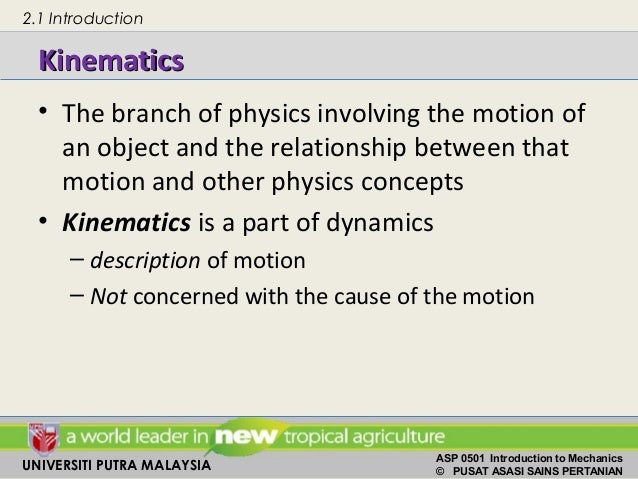
Kinematics is a section of classical mechanics that describes the movement of points objects and entire groups but does not take into account the forces that affect the entire process. Rather contemplate the information thinking about its meaning and its applications. Some experts refer to the study of.
Look around and you will notice that objects around you are in mechanical motion. The section of mechanics that studies the laws of motion its geometric properties the laws of speeds and accelerations is called kinematics. The branch of mechanics that deals with pure motion without reference to the masses or forces involved in it.






.PNG)


